Modern organizations face increasing security challenges that require them to rethink how they manage physical and digital access. Whether streamlining on-site access or managing cloud permissions, the need for unified, robust security protocols is more important than ever. As companies embrace digital transformation, billing and contract management systems are fundamental to maintaining secure and scalable operations.
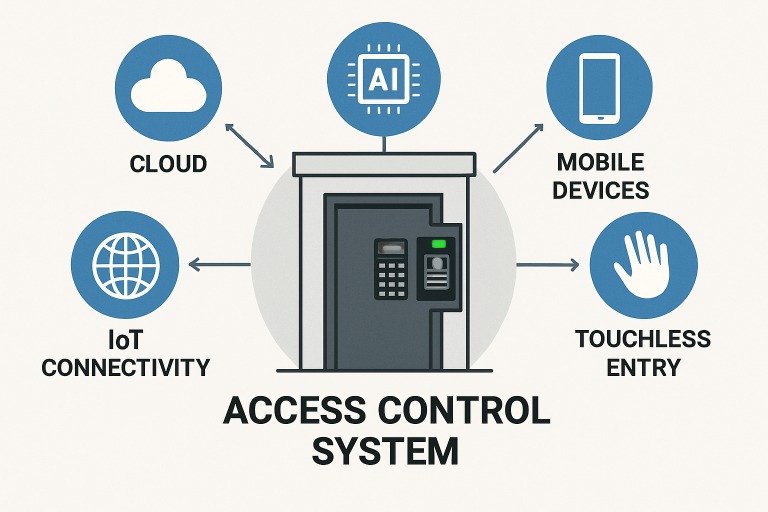
Access control systems now include biometrics, behavioral analytics, and automation, supported by cloud infrastructure and agile frameworks. Organizations must adapt their security strategies to stay ahead of threats and maintain seamless operations. As technology reshapes access control, there’s an increased focus on integrating smart devices, cloud computing, and AI to enhance safety and user experience. Balancing innovation with security is essential for resilience. Cloud security advances enable real-time monitoring, scalability, and centralized management across multiple locations, while maintaining data privacy and reducing operational friction. Transitioning from on-premises to cloud-based access control is a major development, offering instant scalability for organizations of all sizes with centralized dashboards and mobile access. These flexible systems are especially popular in healthcare, education, and large enterprises, ensuring security, agility, and business continuity during disruptions.
AI and Machine Learning
AI and ML are transforming access control by automating decision-making and threat detection. AI systems analyze behavior, identify anomalies, and trigger alerts automatically, helping security teams respond faster and reduce false positives. Machine learning models improve with new data, enhancing accuracy and enabling predictive analytics to identify vulnerabilities early. AI-driven access control is especially effective in high-traffic areas like airports and stadiums, where traditional systems may struggle with throughput without security lapses. Using AI, organizations ensure only authorized users gain access, providing safety and a seamless experience that boosts trust and satisfaction.
Standardization and Interoperability
Historically, access control relied on proprietary systems that caused disconnects and increased integration costs. Recently, efforts focus on open standards and protocols, crucial for organizations seeking unified security that integrates with HR, building management, and third-party services. Standardized platforms reduce vendor lock-in, costs, and simplify updates. Interoperability has become an operational necessity, enabling organizations to respond swiftly to threats, regulations, and growth.
Mobile and Touchless Technologies
With the rise of smart devices, mobile access credentials are replacing physical cards and key fobs. These contactless options let employees and visitors authenticate via smartphones or wearables, reducing lost credentials and improving hygiene—especially important in healthcare and pandemics like COVID-19. Touchless methods such as facial recognition, QR codes, and Bluetooth support remote work and hybrid policies, reduce surface risks, and streamline access. Integration with mobile platforms allows remote guest access and visitor management, boosting security and convenience.
Integration with IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming access control by integrating smart building tech like cameras, sensors, and motion detectors. These systems provide detailed control over entry points and improve security and efficiency. For example, IoT sensors can trigger lockdowns or alerts automatically, reducing response times and risks. As IoT adoption grows, access control becomes smarter and more adaptable for future needs.
Zero-Trust Security Model
The zero-trust model transforms access control by not trusting anyone or any device by default, inside or outside the network. It requires strict identity checks, ongoing authentication, and least-privilege access for all users and devices accessing protected resources. This reduces insider threats and lateral movement risks, especially with remote work and BYOD policies. Implementing zero trust provides continuous verification, matching today’s flexible work environments.
Conclusion
Access control systems are at the heart of modern security strategy, evolving quickly to address new threats and unlock operational efficiencies. Organizations can stay ahead of the curve by embracing cloud-based solutions, leveraging AI and IoT, prioritizing interoperability, and implementing zero-trust principles. These next-generation access control systems are more secure but are also designed for seamless user experiences, reliability, and future readiness.